Indian Bonsai Delhi
The Indian Bonsai
Delhi.
Welcome to the Blog post “The Indian Bonsai Delhi by Delhi Bonsai”
If you’re a bonsai enthusiast or simply interested in the art form, you’ve come to the right place. Our bonsai studio is run by a 30-year experienced bonsai specialist who has dedicated her career to creating her own modern art form of bonsai. With a passion for the art and a wealth of knowledge, we aim to share our love for bonsai with the world through this blog. Join us on this journey as we explore the beauty and intricacies of the bonsai world. Indulge in……
Indian Bonsai Delhi:
What is this Indian Bonsai Delhi Blog all about?
- Here you will get the latest update of the Bonsai Scene in Delhi NCR.
- The news about World of Bonsai.
- Places to go on Bonsai Vacation.
- Latest Trends.
- Resources for Bonsai, Gift Bonsai material
- Pots
- Fences
- Fountains
- Latest Fertilizers
- Pest Control
- Soil Preparation
- Videos on specific Indian Plants.
How to Make a Bonsai
JACINUA UMBELLATA
Rare plant species, suitable for Indian Climatic conditions. Flowering Tree.
Bonsai Styles
Bonsai the styles are important to gain a basic understanding of shapes and leads us to train Bonsai trees.
Formal upright style
Informal Upright, Windswept,Root over rock, Yamodri, Mame




Plant Species suitable for Bonsai in Indian conditions
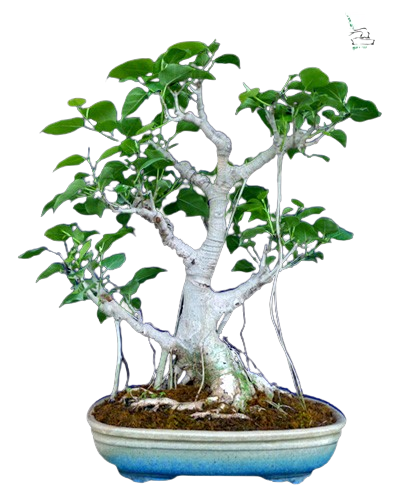
Common Name: Bodhi Vriksha
Scientific Name: Ficus religiosa
MYTHOLOGICAL, MYSTICAL, DRAWS POSITIVE ENERGIES
One of the most desirable trees for bonsai is the bodhi tree, known for its resilience and rapid growth. It boasts stunning bronze-green heart-shaped leaves that have a glossy shine to them. A unique feature of the bodhi tree is its ability to form aerial roots. For optimal growth, place the bodhi tree in a location that receives a minimum of six hours of direct sunlight daily. As a tropical tree, the bodhi thrives in warm temperatures and enjoys basking in the sun.
Soil: The bodhi tree prefers well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. A mix of coarse sand, peat moss, and perlite can work well. Avoid using heavy clay soils or soils that retain too much moisture.
Watering: Water your bodhi tree thoroughly, but allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings.
Overwatering can lead to root rot, so make sure the pot has adequate drainage holes. The frequency of watering will depend on factors such as humidity, temperature, and soil type.
Fertilizer: During the growing season (spring to fall), fertilize your bodhi tree every two weeks with a balanced liquid fertilizer. Reduce fertilization during the winter months when the tree is dormant.
Pruning and Training: Prune your bodhi tree regularly to maintain its shape and encourage branching. You can also use wire to train the tree’s branches and trunk into the desired shape.
Repotting: Repot your bodhi tree every 2-3 years, or when you see the roots circling the pot. Repotting should be done during the spring or early summer, and the tree should be pruned back by one-third to prevent stress.
Pests and Diseases: Watch out for common bonsai pests such as aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs. Treat any infestations promptly with an insecticide or by washing the tree with a gentle soap and water solution. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to fungal diseases such as root rot.
Overall, the bodhi tree is a beautiful and rewarding tree to grow as a bonsai. With proper care, it can thrive and provide a sense of calm and serenity to your home or garden

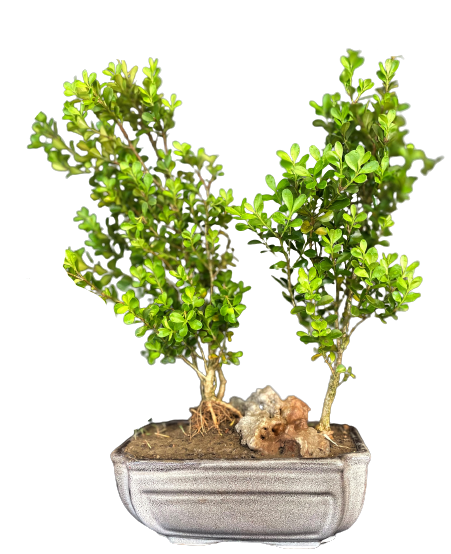
Common Name: Boxwood
Scientific Name:Buxus
FRIENDSHIP TREE.
Boxwood is a genus of evergreen shrubs and small trees that are commonly used for hedging, topiary, and as specimen plants in gardens and landscapes. Boxwoods are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, and they are valued for their dense foliage, fine texture, and versatility.
Boxwood trees are slow-growing and can reach heights of up to 20 feet, but most cultivated varieties are smaller and used for hedges or topiary. Boxwoods have small, oval-shaped leaves that are dark green and glossy, and their bark is smooth and brownish-gray. Boxwoods are also known for their hardiness and tolerance to pruning, making them popular among gardeners and landscapers.
One of the unique characteristics of boxwood trees is their ability to be pruned into various shapes and sizes. Boxwoods are commonly used for topiary, where they can be trained into balls, cones, spirals, and other geometric shapes. Boxwoods are also a popular choice for hedging, where they can create a formal or informal boundary and provide privacy and screening.
Boxwood trees require well-draining soil and partial to full sun exposure, and they are generally low maintenance. However, boxwoods are susceptible to several diseases, including boxwood blight, which can cause defoliation and branch dieback. Proper pruning and sanitation practices can help prevent disease and keep boxwood trees healthy.
Overall, boxwood trees are a versatile and attractive choice for gardeners and landscapers, offering a range of uses and benefits in a variety of settings

Common Name: Baobab / Kalp Vriksha
Scientific Name:Adansonia digitata
MYTHOLOGICAL, MYSTICAL, POWER HOUSE OF ENERGIES
Adansonia is a genus of deciduous trees known as baobabs. Baobabs are native to Africa, Madagascar, Australia, and Arabia, and they are known for their unusual and distinctive appearance, as well as their cultural and ecological importance.
Baobabs are remarkable for their massive, swollen trunks, which can reach up to 30 meters (98 feet) in circumference, making them one of the widest trees in the world. The trunks are adapted to store water during periods of drought, and they can also serve as a source of food, medicine, and shelter for humans and wildlife.
The baobab tree has several unique features that set it apart from other trees. For instance, its leaves are compound and can grow up to 20 centimeters (8 inches) long, while its flowers are large, showy, and pollinated by bats or moths at night. Baobab fruit is also a significant source of nutrition for humans and animals, containing high levels of vitamin C, potassium, and calcium.
The Adansonia tree is also known for its longevity, with some specimens living for over 2,000 years. In many African cultures, baobabs are revered as sacred trees, and they have numerous spiritual and cultural associations. For example, baobab trees are often used as meeting places, places of worship, or places to bury ancestors.
Overall, Adansonia or baobab trees are fascinating and essential trees that play a crucial role in the ecology and culture of the regions where they grow.

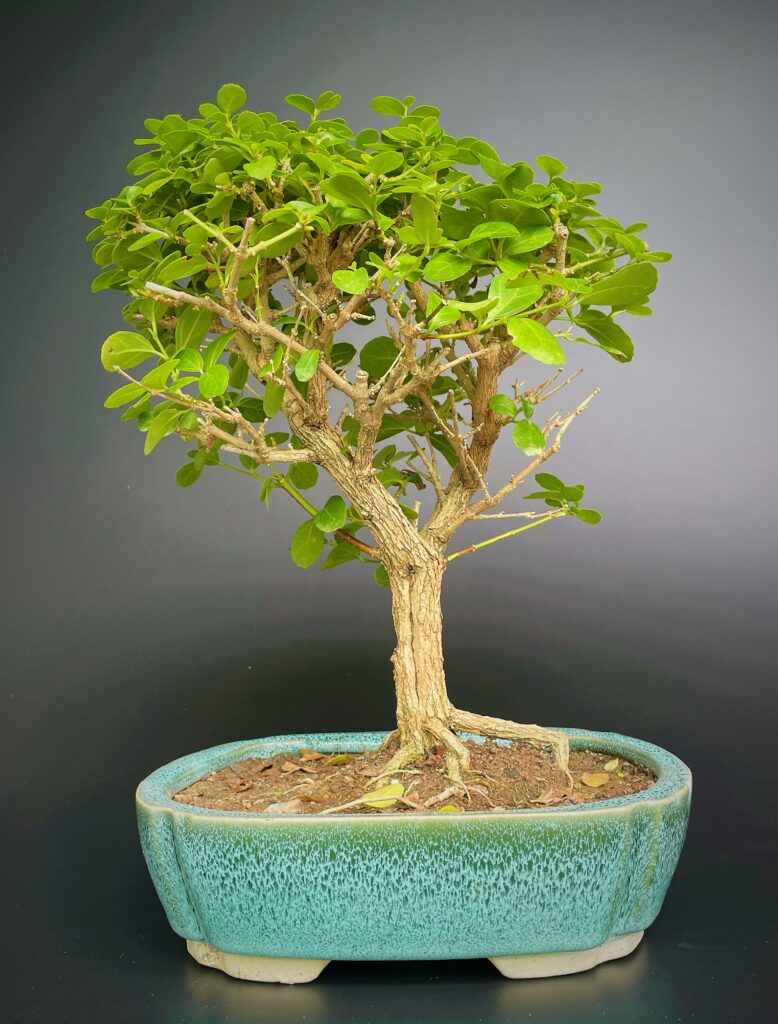
Common Name: Premna
Scientific Name: Premna serratifolia
KAAM DEV TREE
Premna is a genus of plants in the Lamiaceae family that includes over 200 species of trees, shrubs, and herbs. These plants are distributed across tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. The most well-known species in this genus is Premna serratifolia, which is commonly used in traditional medicine for its various therapeutic properties.
Premna serratifolia, also known as Arni or Chinese Waterberry, is a small tree that grows up to 10 meters tall. It has dark green, glossy, and serrated leaves that are used in traditional medicine to treat fever, cough, cold, and inflammation. The bark and roots of the plant are also used for their medicinal properties, including their ability to lower blood sugar levels, improve digestion, and promote wound healing.
In addition to its medicinal uses, Premna serratifolia is also grown for its ornamental value. Its leaves are commonly used in flower arrangements and its small, white or light pink flowers are attractive to pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
Premna plants prefer moist, well-drained soil and partial shade to full sun exposure. They are relatively low maintenance and can be grown in pots or as part of a garden or landscape. Propagation is typically done through seeds or cuttings.
Overall, Premna plants are versatile and valuable for their medicinal and ornamental uses. They are a popular choice for traditional medicine and are increasingly being studied for their potential pharmacological properties

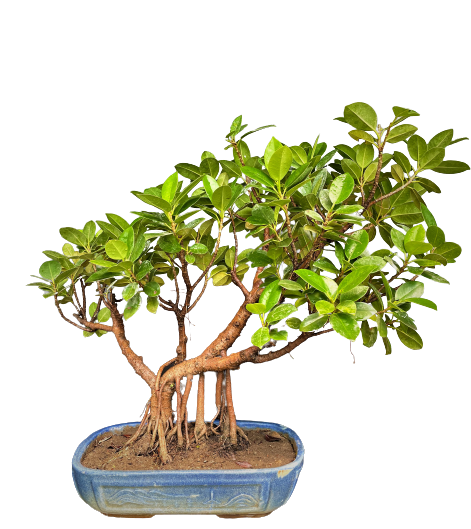
Common Name: Ficus species
Scientific Name: Retusa, Benjamina, Nuda, Microcarpa, Ginsing, Longisland, Island, Starlight,
Air Purifying Bonsai, Landscape Bonsai, Forest style, Gift Bonsai, Attracts positive vibes and energies.
Ficus species are widely distributed throughout India and are an important part of the country’s flora and traditional medicine. Some of the most commonly found species of Ficus in India include:
Ficus religiosa: Also known as the Peepal tree, this species is considered sacred in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It is commonly found in temple courtyards and along roadsides and is often planted for its environmental benefits such as air purification and soil stabilization.
Ficus benghalensis: Also known as the Banyan tree, this species is native to India and is characterized by its massive size and extensive aerial root system. It is considered sacred in Hinduism and is often associated with Lord Shiva.
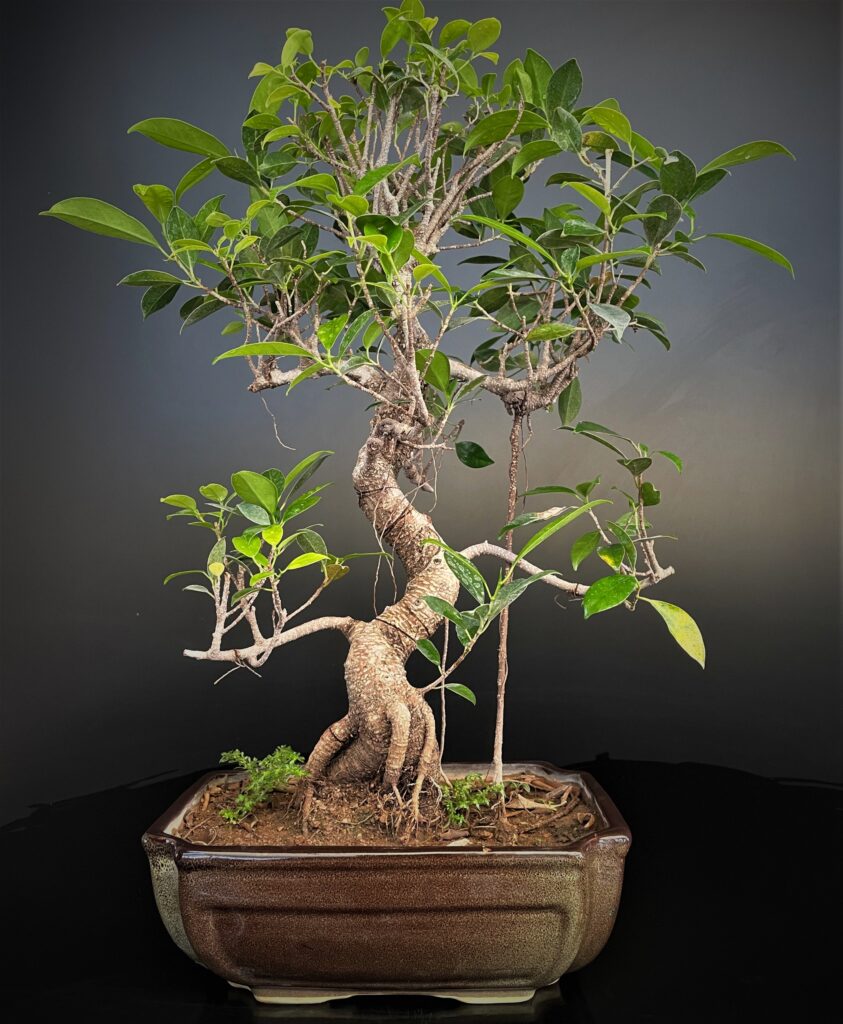
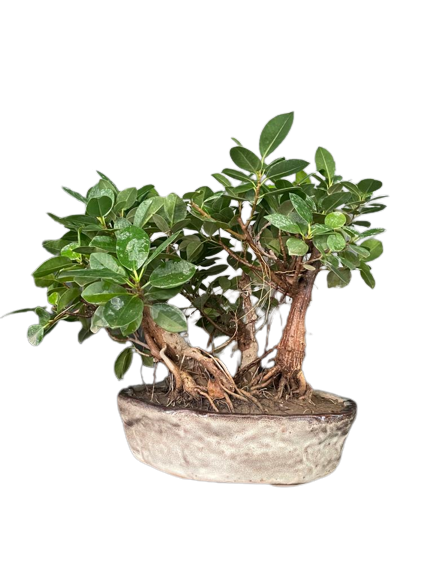
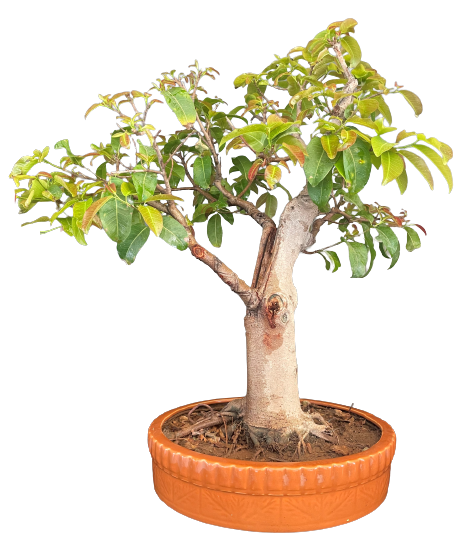





Ficus Species Contd...
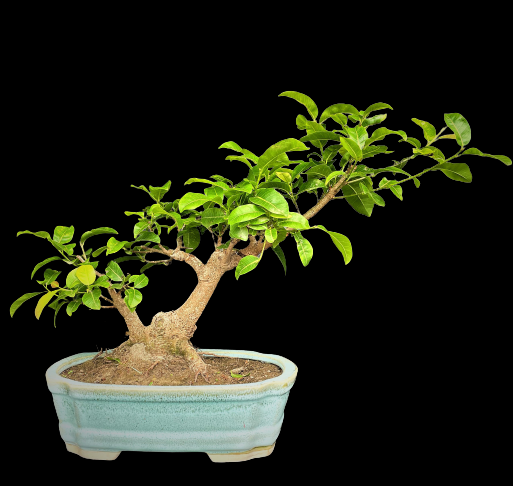

Ficus racemosa: Also known as the Cluster fig, this species is native to India and is characterized by its large, round fruits that grow directly on the trunk and branches. It is used in traditional medicine for its various therapeutic properties.
Ficus carica: Also known as the Common fig, this species is not native to India but has been cultivated in the country for thousands of years. It is commonly used for its edible fruits and is also used in traditional medicine for its laxative and diuretic properties.
In addition to their cultural and medicinal importance, Ficus species are also valued for their environmental benefits such as soil stabilization, erosion control, and carbon sequestration. They are also an important source of food and shelter for wildlife such as birds and monkeys.
Ficus bonsai are also popular in India, and many traditional Banyan trees have been trained into impressive bonsai shapes over the years. Overall, Ficus species play an important role in India’s ecology, culture, and traditional medicine.
Ficus is a genus of plants in the Moraceae family that includes around 850 species of trees, shrubs, and vines. Many species of Ficus are popular among bonsai enthusiasts because of their adaptability, hardiness, and interesting shapes and textures.
Some of the most commonly used Ficus species for bonsai include:
Ficus microcarpa: Also known as the Chinese Banyan or Ginseng Ficus, this species is native to Southeast Asia and is one of the most popular choices for bonsai. It has small, dark green leaves and is characterized by its thick, aerial roots that grow from the trunk and branches.
Ficus benjamina: Also known as the Weeping Fig, this species is native to Southeast Asia and Australia. It has small, glossy leaves and can be trained into a variety of shapes, including upright or cascading forms.
Ficus retusa: Also known as the Indian Laurel or Cuban Laurel, this species is native to tropical Asia and is characterized by its broad, shiny leaves and thick trunk.
Ficus religiosa: Also known as the Sacred Fig or Bo Tree, this species is native to the Indian subcontinent and is considered sacred in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It has heart-shaped leaves and a distinctive aerial root system that can be trained to form interesting bonsai shapes.
Ficus species are generally easy to care for and can be grown indoors or outdoors depending on the specific species and climate. They prefer well-draining soil, regular watering, and occasional fertilization. Ficus bonsai also require periodic pruning and wiring to maintain their shape and promote healthy growth.
Overall, Ficus species are a popular choice for bonsai enthusiasts due to their versatility, interesting shapes, and relative ease of care
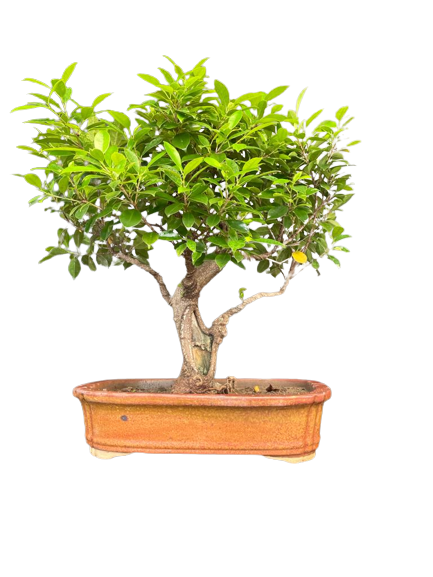
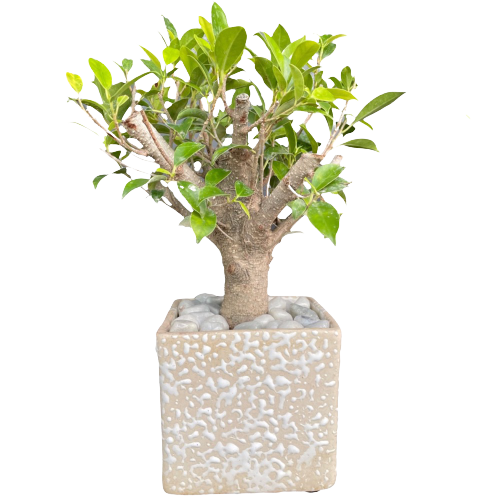
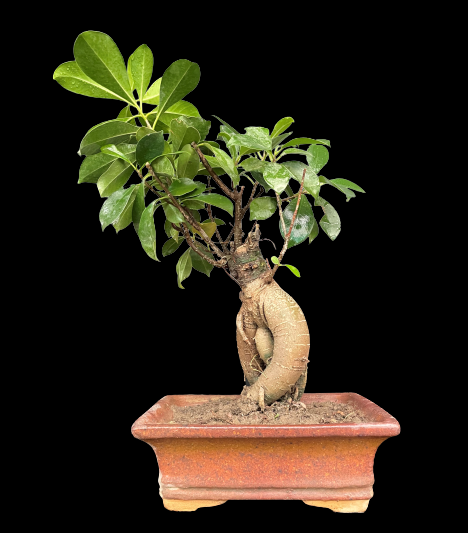
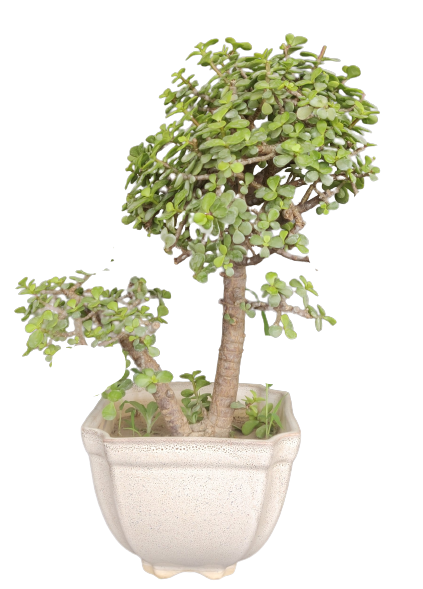




Common Name: Jade
Scientific name: Crassula
Friendship Tree, Creates bonding, Brings love in live, Gives calmness.
Jade plant, also known as Crassula ovata, is a popular succulent plant that is native to South Africa. Here are some key facts about jade plant:
Appearance: Jade plant has thick, fleshy leaves that are oval-shaped and shiny. The leaves are usually a deep green color, although they can also be variegated with red, yellow, or white markings.
Growth: Jade plant can grow up to 3 feet (90 cm) tall and wide. It is a slow-growing plant, but with proper care, it can live for decades.
Care: Jade plant is a low-maintenance plant that is easy to care for. It prefers bright, indirect light and well-draining soil. Overwatering can be harmful to the plant, so it is important to let the soil dry out between waterings.
Propagation: Jade plant can be propagated from stem or leaf cuttings. The cuttings should be allowed to dry out for a few days before being planted in well-draining soil.
Benefits: Jade plant is believed to have a number of health benefits, including improving indoor air quality and reducing stress and anxiety. Some cultures also believe that jade plant brings good luck and prosperity
- Overall, jade plant is a beautiful and easy-to-care-for plant that can bring a touch of greenery and good luck to your home or office.
Below are few species which can trained into a bonsai in Indian Climatic conditions for a successful bonsai making. You can buy bonsais from www.delhibonsai.com and start your journey of happy bonsais.
Chineese Elm
Jamun
Grape wine
gulmohar